
水氮循环过程与机理,农业面源污染与地下水环境
.研究内容:
1)农田生态系统水/氮/盐迁移转化过程与机理;
2)流域面源污染防控与地下水环境;
3) 流域农业水资源可持续利用与综合管理;
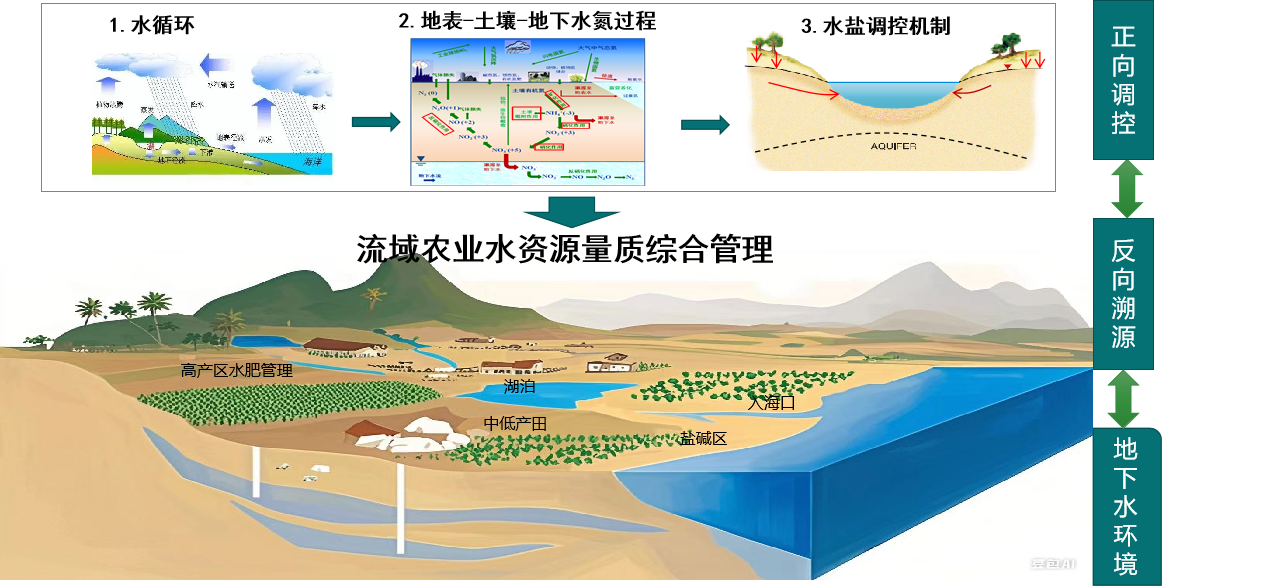
.研究业绩:
主要针对气候变化和人类活动影响下水资源短缺和地下水环境污染等问题,在华北平原水资源量质可持续利用与评价等方面取得了一系列创新性进展;近年来围绕国家需求,在雄安新区农田面源污染和地下水环境监测、治理和保护方面提供了重要的科技支撑。主持国家自然科学基金、国家重点研发计划青年科学家项目、中国科学院先导A类专项、中国科学院引才计划、河北省杰出青年基金、河北省重点研发计划等省级以上项目10余项。共发表论文80余篇,其中Journal of Hydrology,Agricultural Water Management,Water Research等国际主流期刊SCI论文55篇;获发明专利4项,撰写咨询报告8篇。获河北省自然科学奖二等奖、河北省青年科技奖、河北省优秀科技工作者、《地理学报》创刊80周年高被引频次英文论文奖、第36届IAHs会议the best lecture等奖励。
1. Tan KD, Wang SQ*, Zheng WB, Zhang ZX, Liu BX. Geomorphologic and sedimentary features dominate the nitrogen accumulation and leaching in the deep vadose zone from a catchment viewpoint. 2025. Journal of Hydrology
2. Feng WZ, Wang SQ*, Ma Lin, Hu CS. Simulation of spatial and temporal variation of nitrate leaching in the vadose zone of alluvial regions on a large regional scale. 2024, Science of the total environment.
3. Wang S*, Zhang Z., Sprenger M., Wei S., Zheng W., Liu B., Shen Y.*, Zhang Y*. 2024. Seasonal recharge mechanism of the upper shallow groundwater in a long-termwastewater leakage and irrigation region of an alluvial aquifer. Journal of Hydrology.
4. Liu B., Wang S.*, Tian L., Sun H., Liu X. 2023. Response of Soil Nitrate Accumulation and Leaching to Layered Soil Profiles in the Lowland Area of the North China Plain. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition .10.1007/s42729-023-01496-w.
5. Ni P, Wang S*, Liu B, Sun H. 2023. Effects of Organic Manure and Biochar-Based Fertilizer Application on Soil Water and Salt Transport in Brackish Water Irrigated Soil Profile. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition. DOI: 10.1007/s42729-023-01310-7
6. Feng W, Wang S*, Hu C, Li L. 2023. Landform sedimentary contributed to groundwater nitrate vulnerability in multi‑alluvial fan aquifer systems in a watershed. Environmental Earth Sciences 82: 318.
7. Liu M, Guo Y, Zhang X, Shen Yan-Jun, Zhang Y, Pei H, Min L, Wang S, Shen Yanjun. China’s Black Soil Granary is increasingly facing extreme hydrological drought threats. Science Bulletin 68:481-484.
8. Wu Lin, MinLeilei, LiuMeiying, Zhang Yucui, Pei Hongwei, Li Hongjun, Zhang Guanglu, Wang Shiqin, Shen, Yanjun. 2023. Monitoring of thick vadose zone water dynamics under irrigation using a 48 m deep caisson at the Luancheng Critical Zone Observatory. Water Resources Research, 59, e2022WR032965. https://doi. org/10.1029/2022WR032965.
9. Liu F, Zhang J, Wang S, Zou J, Zhen P. 2023. Multivariate statistical analysis of chemical and stable isotopic data as indicative of groundwater evolution with reduced exploitation. Geoscience Frontiers 14: 101476
10. Zheng W, Wang S*, Tan K, Shen Y, Yang L. 2023. Rainfall intensity affects the recharge mechanisms of groundwater in a headwater basin of the North China plain. Applied Geochemistry 155: 105742
11. Lü J, Wang S*, Liu B, Song X. 2023. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of nitrogen transformation potentials in a freshwater estuarine system. Science of The Total Environment 859:160335 doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160335.
12. Lü J,Wang S*, Liu B, Zheng W, Tan K and Song X. 2022. Slight flow volume rises increase nitrogen loading to nitrogen-rich river, while dramatic flow volume rises promote nitrogen consumption, Science of The Total Environment, 844, 157013,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157013, 2022.
13. Liu B, Wang S*, Liu X, Sun H. 2022. Evaluating soil water and salt transport in response to varied rainfall events and hydrological years under brackish water irrigation in the North China Plain. Geoderma, 422: 115954.
14. Liu F, Zhang J. Wang S, Zou J., Zhen P. 2023. Multivariate statistical analysis of chemical and stable isotopic data as indicative of groundwater evolution with reduced exploitation. Geoscience Frontiers 14(1):101476 doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2022.101476.
15. Zheng W, Wang S*. 2021. Extreme precipitation accelerates the contribution of nitrate sources from anthropogenetic activities to groundwater in a typical headwater area of the North China Plain. Journal of Hydrology, 603:127110.
17. Lv J, Niu Y, Yuan R, Wang S. 2021. Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in River Sediments to Water Diversion and Seasonal Changes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 782.
18. Lv J, Yuan R, Wang S. 2021. Water diversion induces more changes in bacterial and archaeal communities of river sediments than seasonality. Journal of environmental management, 293: 112876. DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112876
19. Yang S, Feng W, Wang S, Chen L, Zheng X, Li X, Zhou D. 2021. Farmland heavy metals can migrate to deep soil at a regional scale: A case study on a wastewater-irrigated area in China. Environmental Pollution.281 (15):116977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116977
20. Hou X, Wang S*, Jin X, Li M, Lv M, Feng W. 2020. Using an ETWatch (RS)-UZF-MODFLOW Coupled Model to Optimize Joint Use of Transferred Water and Local Water Sources in a Saline Water Area of the North China Plain. Water. 12.
22. Yuan R, Wang M, Wang S, Song X. 2020. Water transfer imposes hydrochemical impacts on groundwater by altering the interaction of groundwater and surface water. Journal of Hydrology, 583: 124617.
23. Yuan R, Zhang W, Tao X, Wang S, Zhang L. 2020. Coupled effects of high pH and chemical heterogeneity on colloid retention and release in saturated porous media. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 586, 124285.
24. Zheng W, Wang S*, Tan K, Lei Y, 2020. Nitrate accumulation and leaching potential is controlled by land-use and extreme precipitation in a headwater catchment in the North China Plain. Science of the Total Environment, 707, .
25. Yuan R, Zhang W, Tao X, Wang S, Zhang L. 2020. Coupled effects of high pH and chemical heterogeneity on colloid retention and release in saturated porous media. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 586:.
26. Wang S*, Hu Y., Yuan R., Feng W., Pan Y., Yang Y*. 2019. Ensuring water security, food security, and clean water in the North China Plain – conflicting strategies. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 40:63–71
27. Wang S*, Wei S, Liang H, Zheng W, Li X, Hu C, Currell MJ, Zhou F, Min L. 2019. Nitrogen stock and leaching rates in a thick vadose zone below areas of long-term nitrogen fertilizer application in the North China Plain: A future groundwater quality threat. Journal of Hydrology, 576: 28-40.
28. Zheng W, Wang S*, Sprenger M, Liu B, Cao J. 2019. Response of soil water movement and groundwater recharge to extreme precipitation in a headwater catchment in the North China Plain. Journal of Hydrology, 576: 466-477.
29. Liu B, Wang S*, Kong X, Liu X. 2019. Soil matric potential and salt transport in response to different irrigated lands and soil heterogeneity in the North China Plain. Journal of Soils and Sediments.
31. Zhu M, Wang S*, Kong X, Zheng W, Feng W, Zhang X, Yuan R, Song X, Sprenger M. 2019. Interaction of Surface Water and Groundwater Influenced by Groundwater Over-Extraction, Waste Water Discharge and Water Transfer in Xiong’an New Area, China. Water, 11: 539.
32. Adebowale T, Surapaneni A, Faulkner D, McCance W, Wang S, Currell M. 2019. Delineation of contaminant sources and denitrification using isotopes of nitrate near a wastewater treatment plant in peri-urban settings. Science of the Total Environment, 651: 2701-2711.
33. Fu J, Wu Y, Wang Q, Hu K, Wang S, Zhou M, Hayashi K, Wang H, Zhan X, Jian Y, Cai C, Song M, Liu K, Wang Y, Zhou F, Zhu J. 2019. Importance of subsurface fluxes of water, nitrogen and phosphorus from rice paddy fields relative to surface runoff. Agricultural Water Management, 213: 627-635.
34. Liu M, Chen S, Wang S, Hu C, Liu B. 2019. High-Quality Draft Genome Sequence of Pseudomonas songnenensis L103, a Denitrifier Isolated from a 100-Meter-Deep Aquifer in a Heavily Nitrogen-Fertilized Agricultural Area. Microbiology resource announcements, 8.
35. Min L, Qi Y, Shen Y, Wang P, Wang S, Liu M. 2019. Groundwater recharge under irrigated agro-ecosystems in the North China Plain: From a critical zone perspective. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 29: 877-890.
36. Wang S*, Yuan R, Tang C, Song X, Currell M, Yang Z, Sheng Z. 2018. Combination of CFCs and stable isotopes to characterize the mechanism of groundwater-surface water interactions in a headwater basin of the North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 32: 1571-1587.
37. Kong X, Wang S*, Liu B, Sun H, Sheng Z. 2018. Impact of water transfer on interaction between surface water and groundwater in the lowland area of North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 32: 2044-2057.
38. Chen S, Wang F, Zhang Y, Qin S, Wei S, Wang S, Hu C, Liu B. 2018. Organic carbon availability limiting microbial denitrification in the deep vadose zone. Environmental Microbiology, 20: 980-992.
39. Yuan R, Wang S, Yang LH, Liu JR, Wang P, Song XF. 2018. Hydrologic processes of groundwater in a small monsoon-influenced mountainous watershed. Hydrology Research, 49: 2016-2029.
40. Wang S*, Zheng W, Currell M, Yang Y, Zhao H, Lv M. 2017. Relationship between land-use and sources and fate of nitrate in groundwater in a typical recharge area of the North China Plain. Science of the Total Environment, 609: 607-620.
41. Yuan R, Wang S, Wang P, Song XF, Tang CY. 2017. Changes in flow and chemistry of groundwater heavily affected by human impacts in the Baiyangdian catchment of the North China Plain. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76: 19.
42. Wang P, Liu J, Qi S, Wang S, Chen XL. 2017. Tracing sources of nitrate using water chemistry, land use and nitrogen isotopes in the Ganjiang River, China. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 53: 539-551.
43. Wang S*, Tang C, Song X, Yuan R, Han Z, Pan Y. 2016. Factors contributing to nitrate contamination in a groundwater recharge area of the North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 30: 2271-2285.
44. Wang S, Tang C, Song X, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Yuan R. 2014. The impacts of a linear wastewater reservoir on groundwater recharge and geochemical evolution in a semi-arid area of the Lake Baiyangdian watershed, North China Plain. Science of The Total Environment, 482: 325-335.
45. Wang S, Tang C, Song X, Yuan R, Wang Q, Zhang Y. 2013. Using major ions and δ15N–NO3-to identify nitrate sources and fate in an alluvial aquifer of Baiyangdian lake watershed, North China Plain. Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts.
46. Yuan R, Song X, Han D, Zhang L, Wang S. 2013. Upward recharge through groundwater depression cone in piedmont plain of North China Plain. Journal of Hydrology, 500: 1-11.
47. Wang S, Song X, Wang Q, Xiao G, Wang Z, Liu X, Wang P. 2012. Shallow groundwater dynamics and origin of salinity at two sites in salinated and water-deficient region of North China Plain, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 66: 729-739.
48. Yuan R, Song X, Zhang Y, Han D, Wang S, Tang C. 2011. Using major ions and stable isotopes to characterize recharge regime of a fault-influenced aquifer in Beiyishui River Watershed, North China Plain. Journal of Hydrology, 405: 512-521.
49. Liu J, Fu G, Song X, Charles S, Zhang Y, Han D, Wang S. 2011. Stable isotopic compositions in Australian precipitation (vol 116, D04304, 2011). Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 116: 1.
50. Liu J, Song X, Yuan G, Sun X, Liu X, Wang S. 2010. Characteristics of δ18O in precipitation over Eastern Monsoon China and the water vapor sources. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55: 200-211.
51. Song X, Wang S*, Xiao G, Wang Z, Liu X, Wang P. 2009. A study of soil water movement combining soil water potential with stable isotopes at two sites of shallow groundwater areas in the North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 23: 1376-1388.
52. Wang S, Song X, Wang Q, Xiao G, Liu C, Liu J. 2009. Shallow groundwater dynamics in North China Plain. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 19: 175-188. DOI: 10.1007/s11442-009-0175-0.
53. Liu J, Song X, Sun X, Yuan G, Liu X, Wang S. 2009. Isotopic composition of precipitation over Arid Northwestern China and its implications for the water vapor origin. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 19: 164-174.
54. Wang S, Shao J, Song X, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Huo Z. 2008. Application of MODFLOW and geographic information system to groundwater flow simulation in North China Plain, China. Environmental Geology, 55: 1449-1462.
55.Liu J, Song X, Yuan G, Sun X, Liu X, Wang Z, Wang S. 2008. Stable isotopes of summer monsoonal precipitation in southern China and the moisture sources evidence from δ18O signature. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 18: 155-165.
56. 袁瑞强,吕嘉丽,王仕琴. 受引黄影响的河流沉积物细菌群落季节变化. 环境科学学报, 39( 7) : 2190-2199
57. 田路遥,王仕琴*,魏守才,刘丙霞,刘彬彬,胡春胜. 层状包气带黏土层厚度对硝态氮迁移的影响研究.农业工程学报, 36(14)
58. 郑文波,王仕琴*,刘丙霞,雷玉平,曹建生. 基于RZWQM模型模拟太行山低山丘陵区农田土壤硝态氮迁移及淋溶规律, 2019, 40 (4)
59. 王仕琴*,郑文波,孔晓乐. 华北农区浅层地下水硝酸盐分布特征及其空间差异性,中国生态农业学报,2018,26(10)
60. 吕梦宇,王仕琴*,齐永青,华北低平原区降水与坑塘蓄水响应关系研究—以河北省南皮县为例. 自然资源学报,2018,33(10)
61. 袁瑞强, 王亚楠, 王鹏, 王仕琴. 降水集中度的变化特征及影响因素分析——以山西为例. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14 (1): 11-20. doi:10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2017.034
62. 孔晓乐,王仕琴*,丁飞,梁慧雅.基于水化学和稳定同位素的白洋淀流域地表水和地下水硝酸盐来源.环境科学, 2017, 39(6)http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1895.X.20171229.1048.003.html
63. 梁慧雅, 翟德勤, 孔晓乐, 袁瑞强, 王仕琴*. 2017 府河-白洋淀硝酸盐来源判定及迁移转化规律. 中国生态农业学报 25(8), 1236-1244.
64. 梁慧雅,王仕琴*,魏守才. 2017华北山前平原典型厚包气带硝态氮分布累积规律. 土 壤 (Soils), 2017, 49(6): 1179-1186.
65. 赵焕,王仕琴*,孔晓乐,杨永辉. 华北低山丘陵区猪龙河流域地下水水质特征及成因分析. 水文地质工程地质. 2016, 43(2): 17-24.
66. 孔晓乐,王仕琴*,刘丙霞,孙宏勇. 外来调水对华北低平原区地表水和地下水水化学特征的影响—以河北省南皮县为例. 中国生态农业学报. 2016, 24(8):1135-1144.
67. 袁瑞强, 郭威, 王仕琴, 王鹏. 微生物在饱和多孔介质中的迁移. 水资源研究. 2016, 5(4): 334-349.
68. 孔晓乐, 王仕琴*, 赵焕, 袁瑞强.华北低平原区地下水中氟分布特征及形成原因院以南皮县为例[J].环境科学, 2015, 36(11):4051-4058.
69. 袁瑞强,龙西亭,王鹏,王仕琴,宋献方. 白洋淀流域地下水更新速率[J]. 地理科学进展,2015,(03):381-388.
70. 王仕琴,宋献方,王勤学,唐常源,刘昌明. 2014. 华北平原地下水水位微动态变化周期特征分析. 水文地质工程地质. 41(3): 7-14.
71. 宋献方,王仕琴,肖国强,王志民,刘鑫. 2011. 华北平原地下水浅埋区土壤水分动态的时间序列分析. 自然资源学报, 26(1):145-155.
72. 陈宝根,王仕琴,宋献方. 2011. 一维土壤水分运动模拟在土壤水分特征研究中的应用----以华北平原衡水实验站为例. 水文,31(3).
73. 王仕琴,宋献方,肖国强,王志民,刘鑫,王鹏. 2008. 基于氢氧同位素的华北平原地下水浅埋区降水入渗过程研究. 水科学进展, 4:25-31.
74. 王仕琴,宋献方,王勤学,肖国强. 刘昌明. 2008. 华北平原地下水水位动态变化. 地理学报, 63(5):462-472.
75. 王仕琴,邵景力,宋献方,张永波,周小元,霍志彬. 2007. 地下水模型MODFLOW和GIS在华北平原地下水资源评价中的应用. 地理研究, 26(5):2-10.
76. 袁瑞强,宋献方,王鹏,张应华,王仕琴,唐常源. 2012. 白洋淀渗漏对周边地下水的影响. 水科学进展,26:751-756.
77. 柳鉴容, 宋献方, 袁国富, 孙晓敏, 刘鑫, 王仕琴. 2009. 中国东部季风区大气降水 δ^ 18O 的特征及水汽来源. 科学通报,3521-3531.
78. 周小元,张永波,霍志斌,王仕琴. 2008. 地下水资源动态评价机制研究及技术实现. 数水利, 6(6):28-30.
79. 宋献方,柳鉴容,孙晓敏,袁国富,刘鑫,王仕琴,侯士彬. 2007. 基于CERN的中国大气降水同位素观测网络. 地球科学进展,22(7):738-747.
专利:
1) 王光伟,万撒特,王仕琴. 发明专利:一种大气成分采样系统. 授权日:2018年8月21日. 专利号:CN 105784428
2) 王光伟,万撒特,王仕琴. 发明专利:一种大气颗粒物采样系统. 授权日:2019年7月23日. 专利号:CN 106153403 B
|
中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所农业资源研究中心 京ICP备05002857号-1 地址:河北省石家庄市槐中路286号地理位置与乘车路线 邮编:050022 电话:0311-85814521传真:0311-85815093; Email:zhc@sjziam.ac.cn |

|
